Key Takeaways
- The coagulation cascade is a complex series of steps that occurs to form a blood clot.
- Certain genetic variants (SNPs) can increase the clotting cascade and put you at risk of deep vein thrombosis or heart attacks.
- Blood clots can also be caused by infections since inflammatory cytokines released during the immune response can trigger clotting.
- Understanding your genetic propensity towards clotting can help you know what symptoms to look for and when to seek help.
Table 1: My Genetic Variants
| Gene | RS ID | Your Genotype | Effect Allele | Effect Allele Frequency | Notes About Effect Allele |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
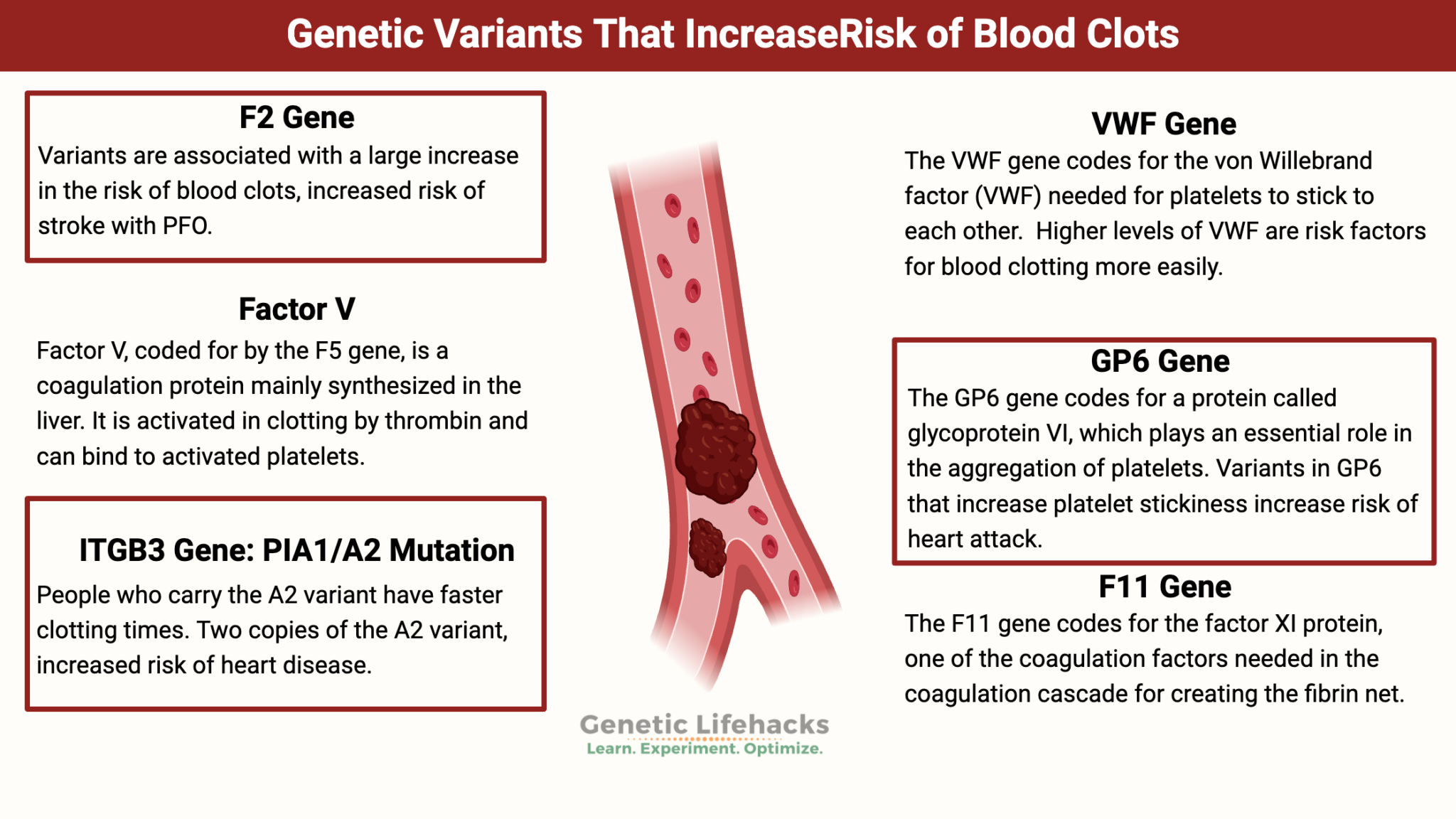
| F2 | rs1799963 | AG | A | 0.01 | Increased risk of blood clots, increased risk of stroke with PFO |
| F2 | i3002432 | -- | A | 0.001 | Increased risk of blood clots, increased risk of stroke with PFO |
| F5 | rs6025 | CC | T | 0.2 | Factor V Leiden; increased risk of clots, DVT |
| ITGB3 | rs5918 | TT | C | 0.14 | PLA1/A2 mutation, increased risk of heart disease |
| VWF | rs1063856 | CT | C | 0.35 | Likely to have increased Von Willebrand factor, slightly increased risk of blood clots |
| VWF | rs1063857 | AG | G | 0.36 | Likely to have increased Von Willebrand factor, slightly increased risk of blood clots |
| GP6 | rs1613662 | GG | G | 0.15 | Increased platelet stickiness |
| F11 | rs2036914 | CT | C | 0.53 | C/C: increased risk of venous thrombosis, thromboembolism |
Lifehacks:
Take the information about your blood clot genetic risk factors as a ‘heads up’.
Don’t ignore the signs of a blood clot. Symptoms of a blood clot in your arm or leg can include swelling, pain, redness, and warmth. If you suspect a clot, head to the doctor for an assessment. While the risk of blood clots increases with age, people genetically prone to clots can get one at any age. Sugar alcohols:
Several studies have recently shown that sugar alcohols, such as erythritol, increase platelet stickiness and clot formation. People in the top quartile (top 25% ) of erythritol consumers are at an increased risk of heart attacks. Interestingly, a study showed that consuming the equivalent of an erythritol-sweetened beverage increased platelet reactivity for more than two days.[ref] A 2024 study showed the mechanism of action for increased platelet reactivity, clotting, and erythritol.[ref] While some question the link between sugar alcohols and platelet reactivity, it is something to consider if you have a genetically increased risk of clots.[ref]
Natural supplements that act as mild blood thinners:
Natural blood thinners may decrease the risk of blood clots. If you are on any prescription medications or under a doctor’s care, check with your doctor before taking supplements that may interact with coagulation.
Curcumin is a natural compound found in turmeric. Studies show that it decreases platelet adhesion and has possible beneficial effects on preventing cardiovascular disease.[ref]
Related article: Curcumin research studies
Aspirin is a natural blood thinner. Talk with your doctor to see if low-dose aspirin might be a good fit for you.
Related article: Aspirin interacts with specialized pro-resolving mediators in the resolution of inflammation
Maslinic acid, a component of olive pomace oil, has recently been shown to downregulate one of the coagulation factors (factor Xa) and decrease platelet aggregation.[ref]
Salidroside, the bioactive component of the herb Rhodiola rosea, has been shown in studies to decrease thrombosis and inhibit platelet function.[ref]
Glycyrrhetinic acid, a component of licorice, directly inhibits factor Xa and is an anticoagulant.[ref]
Nattokinase and Lumbrokinase– These two supplements are natural clot dissolvers. Learn about clinical trials, research, and safety.