Interview Questions
Purpose of these questions (please share this with candidate):
When we interview developers, we have discussions focused on Java and object-oriented design to determine the skill level of a candidate. We don't treat these as tests, nor do we look at the outcome in a pass/fail light. This is simply one more piece of information used in the evaluation process. Please feel free to ask questions and comment on the process.
Java Specific
-
Describe the difference between an
intand anIntegerin Java. When would you use anint, and when would you use anInteger? -
Describe the process of garbage collection in Java. When does an object become a candidate for garbage collection? How do you force the garbage collection process to begin?
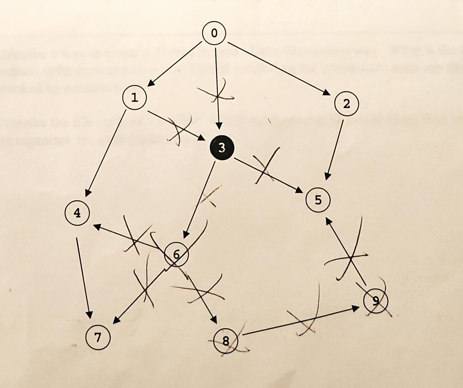
In the following graph, if object 3 is removed, what other objects will become candidates for garbage collection?
- Describe the difference between method overloading and method overriding. Is it possible to overload a static method? Is it possible to override a static method? Talk about the difference between overriding and hiding.
In the following code, explain what the output will be.
public class Base {
public void f() {
System.out.println("Base.f()");
}
public static void g() {
System.out.println("Base.g()");
}
}
public class Child extends Base {
public void f() {
System.out.println("Child.f()");
}
public static void g() {
System.out.println("Child.g()");
}
}
public class Tester {
public static void main(String[] pArgs) {
Base lObj = new Child();
lObj.f();
lObj.g();
}
}-
Describe a way to create a Thread in Java. Describe another way. What is the first method to be executed on a new Thread (excluding the constructor and any methods invoked by constructors)?
-
Describe the life cycle of a servlet. Which methods can be called more than once by the container for a particular servlet class?
General Software Concepts
- In the following simple class, identify any method that is not thread safe. Describe the problem(s), and suggest ways that they could be solved.
public class Simple {
protected int mMember = 0;
public void f(int pParam) {
int lValue = 5;
lValue = lValue + pParam;
System.out.println("f computed " + lValue);
}
public void g(int pParam) {
int lValue = 1;
mMember += lValue * pParam;
System.out.println("g computed " + mMember);
}
}- Two interfaces are defined to represent a binary tree. A binary tree is a tree in which each node can have at most two children. Write the implementation for the method Node.traverse() and the method Tree.traverse(). The methods should implement a depth first traversal of a given tree. Tree.traverse() should be less than three lines of code, and Node.traverse() should be less than ten.
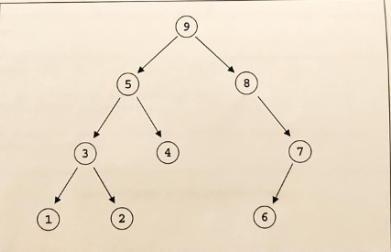
Figure 1: Order in which Node.operate() is called during a DFS
public interface INode {
// These methods return null if there is no child node
public INode getLeftChild();
public INode getRightChild();
/**
* Traverse this node.
* @return void
*/
public void traverse();
public void operate();
}
public interface ITree {
public INode getRootNode();
/**
* DFS traverse the tree from the root node.
*/
public void traverse();
}Figure 2: Definition of interfaces INode and ITree
Following is a code snippet illustrating how the ITree interface might be used to traverse a tree:
public void f() {
// get a tree in some magical way
ITree myTree = getTree();
// traverse the entire tree, starting from the root node
myTree.traverse();
}Figure 3: Example of using ITree and INode.
Experience Based Questions
-
What are design patterns? Why are design patterns useful? Describe a design pattern that you have used in the past.
-
What kept you awake at night in your last job/project?
-
Describe a development process/methodology that you are familiar with (e.g., XP, RUP, etc.). Do you have strong opinions about which of these is best?